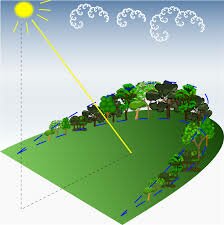
The solar radiation energy that reaches the Earth from the Sun is called insolation [Insolation Meaning in hindi called suryataap(सूर्यताप)]. This energy reaches the Earth in the form of short waves from the Sun. At the outer boundary of the atmosphere, 1.94 calories of heat is received per minute per square cm from the Sun. Albedo is the ratio between the amount of insolation received by a surface and the amount of insolation that is diverted from the same surface. This conversion of solar radiation takes place in short waves.

About 32% of the solar radiation received at the outer boundary of the atmosphere is converted from the surface of the clouds and scattered by dust particles and returns to space. About 2% of the Sun’s heat is reflected from the surface and goes back into space. Thus 34% of the solar radiation is not used for heating the surface.
At the time of total cloud cover, the root cause of reduction in sunlight is change, not absorption. Earth receives 51% of the energy transmitted by solar radiation. Atmosphere captures only 14% of solar energy.
The atmosphere warms and cools in the following ways:
Radiation:
Radiation is the direct heating of a substance by the transmission of heat waves. For example, the Earth and its atmosphere are heated by the rays received from the Sun. It is the only process by which heat can travel through void without any medium. The rays coming from the sun are short waves, which pass through the atmosphere without overheating it and reach the earth. A large part of the rays that have reached the earth goes back into the atmosphere. This is called terrestrial radiation. Terrestrial radiation is a long-wave ray, which is easily absorbed by the atmosphere. Therefore, the atmosphere is hotter than the terrestrial radiation coming from the sun.
Conduction :
When two objects up to the sky come in contact with each other, heat flows from the object of higher temperature to the object of lower temperature. This flow of heat continues until the temperature of both the objects becomes the same. Air is a poor conductor of heat, so the conduction process is the least important for heating the atmosphere. This heats only the lower layers of the atmosphere.
Convection :
The transfer of heat from one part of a gaseous or liquid substance to another by its molecules is called convection. This communication occurs in gases and liquids because the bond between their molecules is weak. This process does not occur in solids.
When the lower layer of the atmosphere is heated by terrestrial radiation or conduction, its air expands which reduces its density. As the density decreases, it becomes lighter and rises to the top. Thus that air carries the heat of the lower layers up. The cold air above comes down to take its place and after some time it also becomes hot. In this way the atmosphere keeps on heating up from the bottom up by the process of convection. It plays a major role in warming the atmosphere.
Advection :
In this process heat is transferred in a horizontal direction. When warm air masses move to colder areas, it heats them up. Due to this, heat is also transmitted from low latitudinal regions to high latitudinal regions. Ocean currents driven by the wind also transmit heat from the tropics to the polar regions.
Isotherm :
It is an imaginary line joining places of equal temperature. The isotherms and temperature distribution have the following characteristics:
Isotherms are drawn roughly parallel to the latitudes in the east-west direction. The reason for this is that all the places located at the same latitude receive the same amount of insolation and the temperature is also almost the same.
Temperatures vary from place to place in the water, so isotherms on the coast suddenly bend.
In the Southern Hemisphere, the water content is high and there are less temperature differences. In contrast, in the Northern Hemisphere, the water content is less and there are more temperature differences. For this reason, isotherms have less curves in the Southern Hemisphere and their east-west direction is more pronounced.
The distance between the isotherms can be used to estimate the temperature gradient (rate of change of temperature). If the isotherms are closer to each other, the heat-prone is greater. Conversely, if the isotherms are farther away from each other, the heat-prone is less.
The temperature is higher in the tropical regions, so the isotherms of higher value are in the tropics. The temperature in the polar regions is very low, so there are isotherms of low value.
The minimum or maximum temperature is found in the months of January and July for most of the regions of the world. This is the reason why these two months are often chosen for temperature analysis.
Range of Tempreature:
The difference between maximum and minimum temperature is called temperature difference. It is of two types:
Daily Range of Tempreature:
The difference between the maximum and minimum temperature at a place in a day is called the daily temperature. This difference in temperature is called the temperature range.
Annual Range of Tempreature:
Just as there is a difference between day and night temperatures, there is also a difference between summer and winter temperatures. Therefore, the difference between the mean temperature of the hottest and the coldest month of a place is called the annual range of temperature. The highest annual temperature difference in the world is 65.5 centigrade in a place called Bykhroyansk located in Siberia.
The difference between the average temperature of a particular place and the average temperature of its latitude is called thermal anomaly.